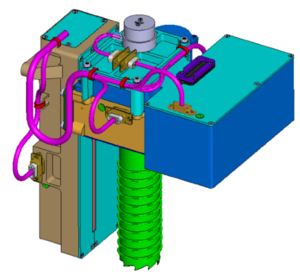
Lunar Volatiles Scout (LVS)
The LVS is an instrumented drill for in-situ characterisation of planetary soil samples and volatiles. The cavity drill can be used to drill into icy regolith to a depth of about 10 cm. The enclosed regolith is then heated to >400 °C with the help of an integrated heating element to release volatile substances such as water. A built-in miniaturised ion trap mass spectrometer (ITMS) and pressure sensors allow live analysis of the evolved gases. Due to the minimal manipulation of the sample, the risk of losing volatile substances during the otherwise necessary sampling is avoided. This allows characterisation of the sample in its pristine state, which is a significant advantage over conventional instruments for analysing soil samples.
The main application of the LVS is for prospecting volatile lunar resources, such as water. Its low mass and volume allow it to be used on mobile rovers to cover large areas on the lunar surface. The LVS can also be used on stationary platforms and in the environment of other atmosphereless celestial bodies.
Funding:
- European Comission Horizon 2020 (2016-2022)
- ESA (2020-2021)
- DLR (2012-2016, 2019-2021)
Partners:
- OHB System (DE)
- The Open University (UK)