- Combining VLBI and ring laser observations for determination of high frequency Earth rotation variation. Journal of Geodynamics 62 (12), 2012, 6973 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Precision and accuracy of GPS-derived station displacements. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth 53-54, 2012, 72-79 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Determination of the Earth's Pole Tide Love Number k2 from Observations of Polar Motion Using an Adaptive Kalman Filter Approach. Journal of Geophysical Research 117 (B09), 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- A wavelet based approach for monitoring plantation crops (tea: Camellia sinensis) in North East India. International Journal of Remote Sensing 33 (16), 2012, 4982-5008 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Self-locked operation of large HeNe ring laser gyroscopes. Metrologia 49 (3), 2012, 209-212 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Consistent patterns of Antarctic ice sheet interannual variations from ENVISAT radar altimetry and GRACE satellite gravimetry. Geophysical Journal International 189 (2), 2012, 863-876 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Impact of combining GRACE and GOCE gravity data on ocean circulation estimates. Ocean Science 8 (1), 2012, 65-79 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Scientific rationale and development of the Global Geodetic Observing System. Geodesy for Planet Earth, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- GGOS Bureau for Standards and Conventions: Integrated standards and conventions for geodesy. Geodesy for Planet Earth, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Impact of albedo radiation on GPS satellites. Geodesy for Planet Earth, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Using atmospheric uncertainties for GRACE de-aliasing: first results. Geodesy for Planet Earth, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Future satellite gravity field missions: feasibility study of post-Newtonian method. Geodesy for Planet Earth, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Mass variations in the Siberian permafrost region from GRACE. Geodesy for Planet Earth, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Using Swarm for gravity field recovery: first simulation results. VII Hotine-Marussi Symposium on Mathematical Geodesy, IAG Symposia, Springer, 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Apparent clock variations of the Block IIF-1 (SVN62) GPS satellite. GPS Solutions 16 (3), 2012, 303-313 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Note: Electronic circuit for two-way time transfer via a single coaxial cable with picosecond accuracy and precision. Review of Scientific Instruments 83 (11), 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Time-variable Gravity Field: Contributions of GOCE Gradiometer Data to Monthly and Bi-Monthly GRACE Gravity Field Estimates. , 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext (mediaTUM)
- The application and potential of Bayesian network fusion for automatic cartographic mapping. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 2012 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
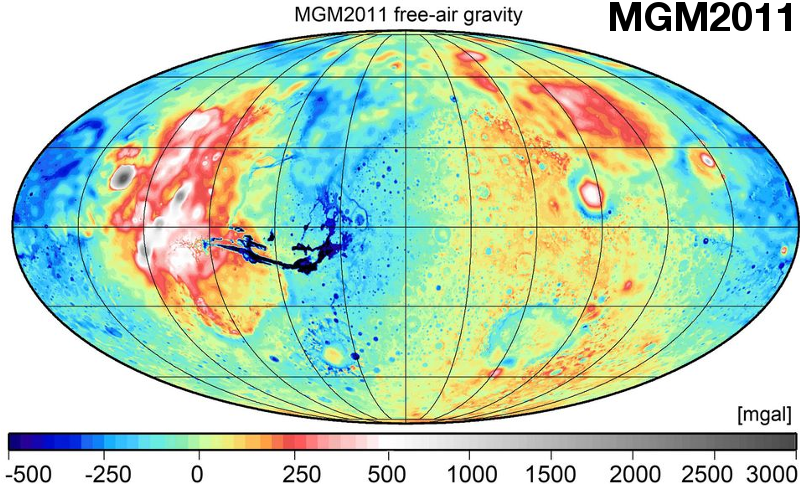
- Indirect evaluation of Mars Gravity Model 2011 using a replication experiment on Earth. Studia Geophysica and Geodetica 56, 2012, 957-975 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
- Regional Geoid-based Vertical Datums - Some Australian Perspectives. Journal of Geodetic Science, Special Issue on Vertical Datum 4 (2), 2012, 370-376 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
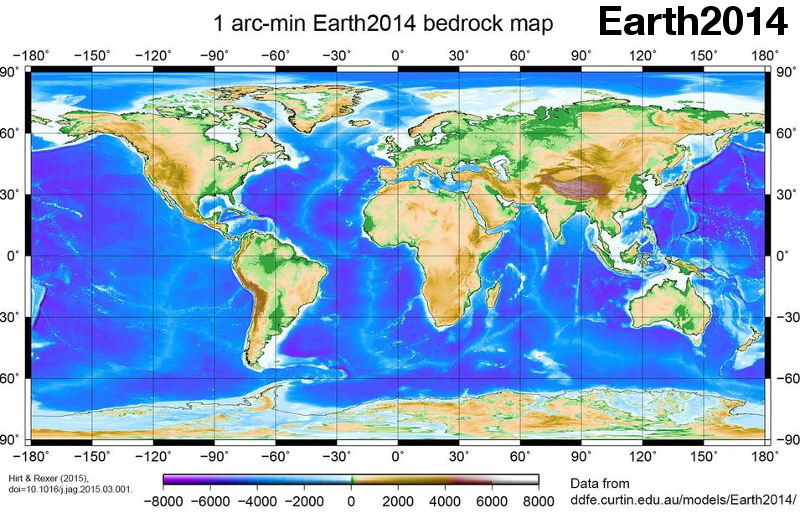
- Evaluation of high-degree series expansions of the topographic potential to higher-order powers. Journal Geophysical Research (JGR) – Solid Earth 117, 2012, B12407 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
- Die GETRIS Mission Konzeptstudie einer zukünftigen Schwerefeldmission zur Beobachtung von Massentransportprozessen im System Erde. Centre of Geodetic Earth System Research, 2012, mehr… BibTeX Volltext (mediaTUM)
- Research and Development Programme 2011 2015. Centrum für Geodätische Erdsystemforschung, 2012, mehr… BibTeX Volltext (mediaTUM)
- A 1.5 km-resolution gravity field model of the Moon. Earth Planet Science Letters 329-330, 2012, 22-30 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
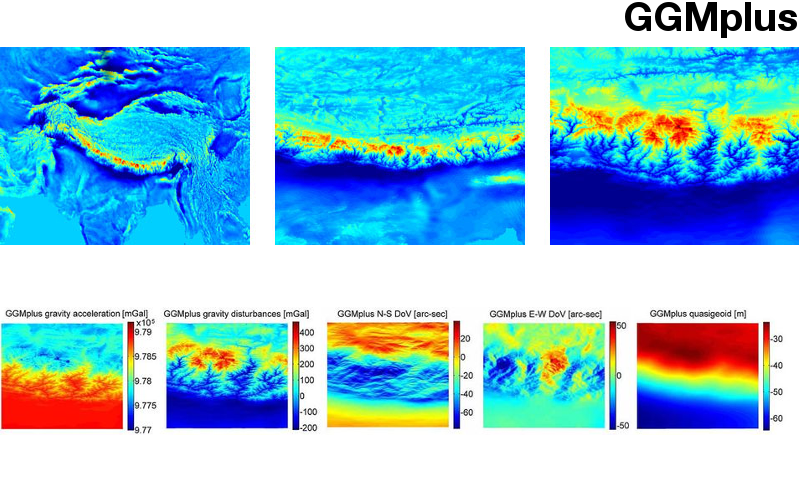
- Topographic/isostatic evaluation of newgeneration GOCE gravity field models. , Journal Geophysical Research (JGR) – Solid Earth 117, 2012, B05407 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
Ingenieurinstitut für Astronomische und Physikalische Geodäsie
Das Ingenieurinstitut besteht aus:

Lehrstuhl für Astronomische und Physikalische Geodäsie
Univ.-Prof. Dr.techn. Mag.rer.nat. Roland Pail

Professur für Satellitengeodäsie
Univ.-Prof. Dr.phil.nat. Urs Hugentobler