- Prediction versus real-time orbit determination for GNSS satellites. GPS Solutions 23 (39), 2019 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- The adjusted optical properties for Galileo/BeiDou-2/QZS-1 satellites and initial results on BeiDou-3e and QZS-2 satellites. Advances in Space Research 63 (5), 2019, 1803--1812 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Decawave UWB Clock Drift Correction and Power Self-Calibration. Sensors 19 (13), 2019, 2942 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Unique 4-DOF Relative Pose Estimation with Six Distances for UWB/V-SLAM-Based Devices. Sensors 19 (20), 2019, 4366 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Improved Time of Arrival measurement model for non-convex optimization. NAVIGATION 66 (1), 2019, 117-128 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Mechanism of error propagation from the subdaily Universal Time model into the celestial pole offsets estimated by VLBI. Advances in Space Research 63 (1), 2019, 51-62 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- 20. Internationale Geodätische Woche Obergurgl, 2019 – Die Bestimmung physikalischer Höhen mit Satelliten. In: 20. Internationale Geodätische Woche Obergurgl, 2019. Wichmann, 2019, 59-68 mehr… BibTeX
- Applicability of NGGM near-real time simulations in flood detection. Journal of Geodetic Science 9 (1), 2019, 111-126 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Cap integration in spectral gravity forward modelling: near- and far-zone gravity effects via Molodensky's truncation coefficients. Journal of Geodesy 93 (1), 2019, 65--83 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Seismic Evidence for Plume‐Slab Interaction by High‐Resolution Imaging of the 410‐km Discontinuity Under Tonga. Geophysical Research Letters 46 (23), 2019, 13687-13694 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Southward propagation of Nazca subduction along the Andes. Nature 565 (7740), 2019, 441-447 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- GNSS Orbit Prediction with Enhanced Solar Radiation Pressure Model. China Satellite Navigation Conference, 2019 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
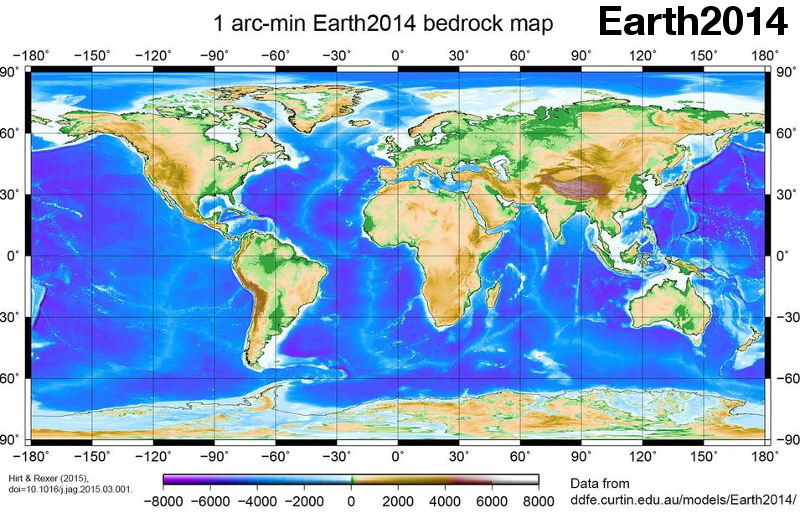
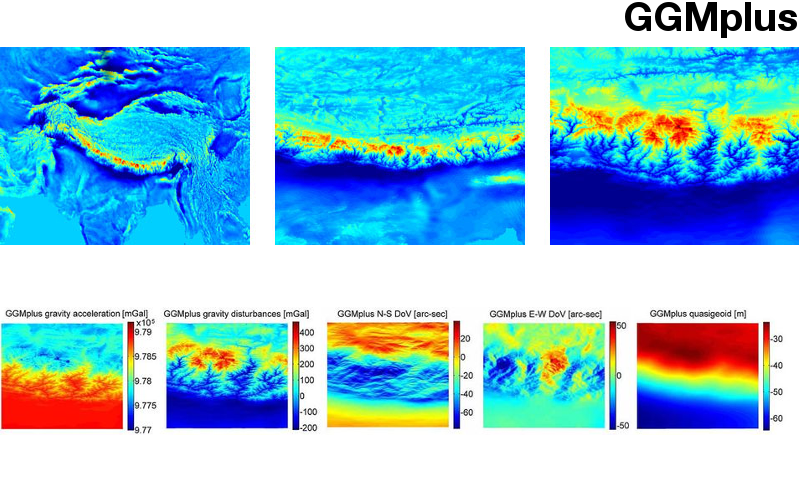
- SRTM2gravity: An Ultrahigh Resolution Global Model of Gravimetric Terrain Corrections. Geophysical Research Letters 46 (9), 2019 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI ) Volltext (mediaTUM)
- SPOOK - A comprehensive Space Surveillance and Tracking analysis tool. Acta Astronautica 158, 2019, 178-184 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Impact of a novel hybrid accelerometer on satellite gravimetry performance. Advances in Space Research 63 (10), 2019, 3235 - 3248 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Regional gravity field recovery of the void areas using SGG-derived surface residual gravity disturbances based on least-squares collocation: a case study in Iran. Journal of Applied Geophysics 164, 2019, 40 - 52 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Next generation gravity missions: near-real time gravity field retrieval strategy. Geophysical Journal International 217 (2), 2019, 1314-1333 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- A Global Height System – Following Heinrich Bruns (1878). zfv – Zeitschrift für Geodäsie, Geoinformation und Landmanagement (1/2019), 2019, 17–24 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- On the assimilation of absolute geodetic dynamic topography in a global ocean model: impact on the deep ocean state. Journal of Geodesy 93 (2), 2019, 141--157 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Influence of subdaily model for polar motion on the estimated GPS satellite orbits. Journal of Geodesy 93 (2), 2019, 229--240 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Divergence-free spherical harmonic gravity field modelling based on the Runge--Krarup theorem: a case study for the Moon. Journal of Geodesy 93 (4), 2019, 489--513 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- A numerical study of residual terrain modelling (RTM) techniques and the harmonic correction using ultra-high-degree spectral gravity modelling. Journal of Geodesy 93 (9), 2019, 1469--1486 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- GOCE gradiometer data calibration. Journal of Geodesy 93 (9), 2019, 1603--1630 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Cap integration in spectral gravity forward modelling up to the full gravity tensor. Journal of Geodesy 93 (9), 2019, 1707--1737 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
- Residual least-squares collocation: use of covariance matrices from high-resolution global geopotential models. Journal of Geodesy 93 (9), 2019, 1739--1757 mehr… BibTeX Volltext ( DOI )
Ingenieurinstitut für Astronomische und Physikalische Geodäsie
Das Ingenieurinstitut besteht aus:

Lehrstuhl für Astronomische und Physikalische Geodäsie
Univ.-Prof. Dr.techn. Mag.rer.nat. Roland Pail

Professur für Satellitengeodäsie
Univ.-Prof. Dr.phil.nat. Urs Hugentobler