Smart Sustainable Districts (SSD)
Smart, Sustainable Districts (SSD) aims to partner with the most ambitious district level developments in the cities and regions represented in the Climate-KIC. It will offer Climate-KIC partners the opportunity to co-develop and demonstrate how new thinking, coupled with effective tools, technologies and policies, can lead to factor-4 improvement in city district performance across a range of sustainability measures.
Project description
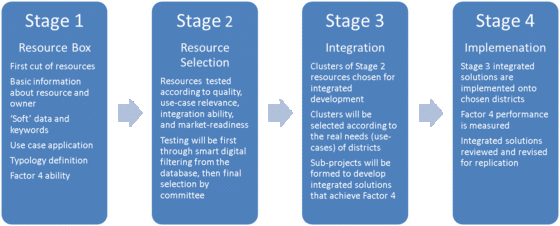
The programme has structured project phases of three years each. The focus of SSD in the first three year phase will be on three things: first, collating the tool box of Climate-KIC partner products and services; second, developing new ways of integrating the tools and services to provide factor 4 improvements; and third, co-developing and applying these innovations with the four selected districts. The projects’ added value comes primarily from the second two and this is where most effort is focussed. It will provide added value in areas where significant investment is already delivering, or planned to deliver, exemplar developments. It will focus on both a dramatic level of integration, across much of the Climate-KIC portfolio, and substantial co-development with the most significant district projects in Europe. It will be used as a test-bed for replication of sustainable smart city systems delivery in other cities.
The SSD programme focuses on how systems interact to identify the opportunities for radical improvement in performance. The intention is not to simply seek iterative improvement in efficiency, but to seek an 80% improvement (factor 4) in performance outcomes wherever this is available. The SSD partners have a wide range of products and services from this systems-based approach including those that:
- Create of spatial and legal frameworks for implementation of smart technologies (e.g. urban design framework incl. optimized transport system)
- Capture waste heat from electricity grid cables and transformers
- Utilise the potential latent storage capacity in urban transport networks
- Facilitate smart grid technology to optimise the available energy in the grid at any one time based on two way flows of energy and information
- Enable low levels of disruption for retrofitting large-scale commercial buildings
- Integrate and design hydrogen infrastructure into the energy ecology for cities
- Digitally link utilities and services within cities
- Make cities more aware and adaptive in the face of environmental, social and economic challenges
- Track and visualise household-level waste and consumables
- Enhance the climatological interface between buildings and the external environment
- Aggregate demand and manage financial flows through new business model innovations
- Facilitate citizen engagement and behaviour change in all of these critical areas.
- Enhance and interconnect interdisciplinary entrepreneurs as components for a flexible dynamic masterplan to create green urban incubators (urban management as co-evolution)